I’ve worked in the solar energy industry for many years, designing and evaluating systems ranging from small residential installations to large commercial and industrial projects. One of the most frequently asked questions I receive today is about hybrid solar power systems.
When people hear the term “hybrid,” they immediately assume it means better, but the reality is more nuanced.
A hybrid solar power system can be an excellent solution or a costly mistake depending on your goals, location, and energy usage.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through exactly what a hybrid solar power system is, how it works, how much it costs, the advantages and disadvantages, and how to decide if it’s the right choice for your home or business.
I’ll also explain where hybrid systems fit compared to grid-tied and off-grid solar systems, based on real-world design experience, not marketing hype
What Is a Hybrid Solar Power System?
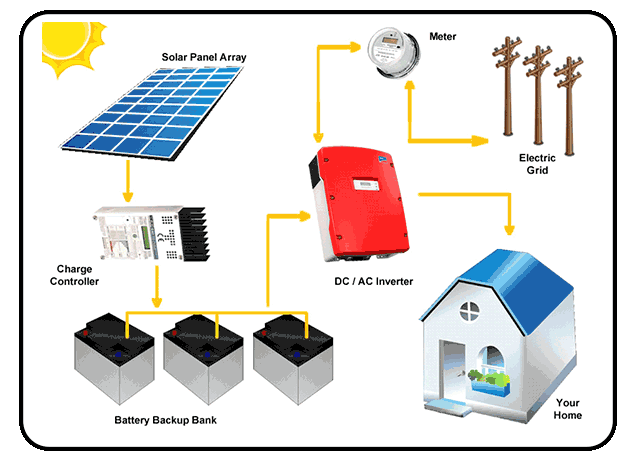
A hybrid solar power system is a solar setup that combines:
- Solar panels
- A battery storage system
- A connection to the utility grid
In simple terms, it sits between a grid-tied system and an off-grid system.
Unlike a standard grid-tied system, a hybrid system includes batteries, allowing you to store excess solar energy for later use.
Unlike a fully off-grid system, it still stays connected to the utility grid as a backup or supplemental power source.
This combination gives you flexibility, backup power, and better control over energy usage, but it also adds complexity and cost.
How Hybrid Solar Power Systems Work (Step by Step)
To really understand hybrid solar power systems, it helps to break down how energy flows through the system during different times of the day.
Solar Panels Generate Electricity
Just like any other solar system, everything starts with the solar panels.
- The panels absorb sunlight
- They produce DC (direct current) electricity
- That electricity flows to the inverter
This part is identical to grid-tied and off-grid systems.
Hybrid Inverter Manages Power Flow
The hybrid inverter is the brain of the system.
It performs several functions at once:
- Converts DC electricity from the panels into AC electricity for your home
- Manages battery charging and discharging
- Controls when energy is pulled from or sent to the grid
This is one of the main differences between hybrid systems and simpler solar setups. Hybrid inverters are more advanced and pricier because they do more.
Batteries Store Excess Energy
When your solar panels produce more energy than your home is using, that excess power can be:
- Stored in the batteries
- Exported to the grid
- Used to power loads directly
In most hybrid systems, batteries are prioritized first, especially if the goal is backup power or energy independence.
Later at night or during grid outages, that stored energy can be used to run your home.
Grid Connection Acts as Backup and Supplement
If:
- The batteries are empty, or
- Solar production is low, or
- Your demand exceeds system capacity
…the system automatically pulls power from the grid.
This seamless switching is one of the biggest advantages of hybrid solar power systems. You don’t have to manually intervene, and most systems transition so quickly that you won’t even notice.
What Makes Hybrid Solar Power Systems Different?
To put it simply:
- Grid-tied systems → Cheapest, no backup during outages
- Off-grid systems → Full independence, high cost, complex design
- Hybrid systems → Balance of independence and reliability
Hybrid systems give you partial energy independence without forcing you to oversize your system, the way off-grid installations often require.
Main Components of a Hybrid Solar Power System
From my experience, these are the essential components you’ll find in a properly designed hybrid system.
Solar Panels
These generate electricity from sunlight. Panel type (monocrystalline vs. polycrystalline) matters less than proper sizing and layout.
Hybrid Inverter
This is not a standard grid-tied inverter.
A hybrid inverter must:
- Handle battery charging
- Support islanding (operating during grid outages)
- Coordinate multiple power sources
Popular brands include:
- Sol-Ark
- Victron Energy
- SMA
- Growatt
- GoodWe
Battery Storage System
Batteries are usually lithium-ion today due to:
- Higher efficiency
- Longer lifespan
- Lower maintenance
Battery capacity is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), not watts.
Energy Management System (EMS)
Many modern hybrid systems include software that lets you:
- Monitor energy usage
- Set charging priorities
- Optimize self-consumption
- Reduce peak grid usage
This is especially valuable in areas with time-of-use electricity rates.
Utility Grid Connection
Even though you have batteries, the grid remains available as
- Backup power
- Supplemental energy source
- Export destination for excess solar
Advantages of Hybrid Solar Power Systems
After designing and analyzing many systems, here are the real advantages of hybrid solar power systems, not just marketing claims.
Backup Power During Outages
This is the #1 reason most homeowners choose hybrid systems.
Unlike grid-tied systems that shut down during outages, a hybrid system can continue powering:
- Lights
- Refrigerators
- Internet
- Critical appliances
You don’t need a separate generator for most short outages.
Better Energy Independence
You rely less on the grid, especially during:
- Evenings
- Peak pricing hours
- Blackouts
You still have grid access, but you control when and how you use it.
Optimized Energy Usage
Hybrid systems allow you to:
- Store solar energy during the day
- Use it at night
- Avoid expensive peak electricity rates
This is particularly useful in regions with net metering limitations.
Scalability
Many hybrid systems allow you to do the following.
- Adding more batteries later
- Expanding solar capacity
- Upgrading software features
This flexibility matters if your energy needs grow over time.
Reduced Generator Dependence
In areas where people traditionally rely on diesel or gas generators, hybrid systems dramatically reduce fuel usage.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Solar Power Systems
This is an aspect that many installers tend to overlook.
Hybrid systems are not always the best option.
Higher Upfront Cost
Adding batteries and a hybrid inverter significantly increases cost.
Compared to grid-tied systems, expect:
- Higher equipment costs
- More complex installation
- Longer payback periods
Battery Degradation Over Time
All batteries degrade.
Even high-quality lithium batteries:
- Lose capacity over time
- Eventually needs replacement
- Represent a future expense
This is often underestimated.
Battery Degradation Over Time
All batteries degrade.
Even high-quality lithium batteries:
- Lose capacity over time
- Eventually needs replacement
- Represent a future expense
This is often underestimated.
Not Always Financially Optimal
If your grid is reliable and net metering is generous, a grid-tied system may provide better ROI.
Hybrid systems make the most sense when resilience and control matter more than pure payback.
How Much Do Hybrid Solar Power Systems Cost?
Costs vary widely, but I’ll give realistic ranges based on real-world projects.
Typical Residential Cost Range (U.S.)
$18,000–$35,000+
Depends on:
- Solar array size
- Battery capacity
- Equipment brand
- Installation complexity
Cost Breakdown (Approximate)
- Solar panels: 25–35%
- Batteries: 30–45%
- Inverter & electronics: 15–20%
- Labor, permits, wiring: 10–15%
Batteries are the biggest cost driver.
Commercial Hybrid Systems
Commercial systems can range from $50,000 to several hundred thousand dollars.
These are often used for:
- Peak shaving
- Backup power
- Energy cost optimization
Hybrid Solar vs Grid-Tied vs Off-Grid Systems
This comparison helps clarify when hybrid systems truly make sense.
Grid-Tied Systems
- Lowest cost
- Best ROI
- No backup power
- Dependent on grid availability
Off-Grid Systems
- Full independence
- Highest cost
- Requires careful load management
- No utility bills
Hybrid Systems
- Balanced approach
- Backup power included
- Moderate to high cost
- Flexible energy control
Who Should Consider Hybrid Solar Power Systems?
From my experience, hybrid systems are ideal for:
- Homes with frequent grid outages
- Areas with unreliable utilities
- Locations with poor net metering policies
- Users who want backup without going fully off-grid
- Businesses that need continuity during outages
They are not ideal for:
- People chasing the fastest ROI
- Homes with extremely reliable grids
- Very low electricity usage
Common Design Mistakes I See
Over the years, I’ve seen many hybrid systems fail to meet expectations due to poor design.
Oversizing Batteries Without Need
More batteries ≠ better system.
Undersizing Solar Arrays
Batteries without enough solar input don’t help.
Ignoring Load Prioritization
Critical loads should be separated from nonessential ones.
Choosing Cheap Inverters
Don’t skimp on the inverter, as it serves as the central component of the system.
Maintenance and Lifespan
Hybrid systems are relatively low-maintenance, but not maintenance-free.
- Solar panels: 25+ years
- Hybrid inverter: 10–15 years
- Lithium batteries: 8–15 years (depending on usage)
Regular monitoring and occasional firmware updates are important.
Are Hybrid Solar Power Systems Worth It?
In my professional opinion.
Hybrid solar power systems are worth it when reliability, control, and resilience matter more than the fastest payback.
While hybrid solar power systems are not a universal solution, their proper design provides an excellent balance between energy independence and practicality.
FAQ: Hybrid Solar Power Systems
What is the difference between hybrid and grid-tied solar?
Hybrid systems include batteries and backup power; grid-tied systems do not.
Can a hybrid solar system work without the grid?
Yes, temporarily, but it’s not designed for long-term full off-grid operation unless oversized.
Do hybrid systems qualify for tax incentives?
In many regions, yes, especially if batteries are charged by solar.
How long can a hybrid system power my home?
It depends on battery capacity and load size, anywhere from a few hours to multiple days.
Final Thoughts
Hybrid solar power systems are one of the most versatile and misunderstood solar solutions on the market today.
When designed correctly and for the right reasons, they provide:
- Energy security
- Flexibility
- Long-term resilience
But they must be approached strategically, not emotionally.
If you’re considering solar and want backup power without going fully off-grid, a hybrid system may be the smartest middle ground.